QMET Confirms Second Major Natural Hydrogen Discovery in Nova Scotia's Springhill Area - Soil Gas Samples up to 1,652 ppm
Rhea-AI Summary
Q Precious & Battery Metals (OTC:BTKRF) has announced a significant second natural hydrogen discovery in Nova Scotia's Springhill area. The company's soil gas sampling program yielded impressive results, with 17 samples exceeding 400 ppm hydrogen, including three samples over 700 ppm and a peak measurement of 1,652 ppm.
The discovery was made in collaboration with Quebec Innovative Materials Corp. and Institut National de la Recherche Scientifique (INRS). QMET holds 31 licenses along the northern margin of the Cumberland Basin within the Springhill-Salt Springs-Oxford-Pugwash-Fox Harbour-Wallace region. The best hydrogen values were detected in the Springhill area where the Athol syncline connects to the Oxford Fault, a crustal cutting fault.
While wildfire alerts restricted access to parts of the region, QMET and its partners plan to complete the survey in Fall 2025.
Positive
- Discovery of second major natural hydrogen zone with peak measurements of 1,652 ppm
- 17 soil gas samples exceeded 400 ppm hydrogen, including three over 700 ppm
- Strategic holding of 31 licenses in the Cumberland Basin region
- Partnership with Quebec Innovative Materials Corp. and INRS strengthens exploration capabilities
Negative
- Wildfire alerts limited access to parts of the region, resulting in incomplete survey
- Early-stage exploration with no production or revenue metrics yet
News Market Reaction
On the day this news was published, BTKRF gained 7.12%, reflecting a notable positive market reaction.
Data tracked by StockTitan Argus on the day of publication.
Vancouver, British Columbia--(Newsfile Corp. - September 17, 2025) - Q Precious & Battery Metals Corp. (CSE: QMET) (OTC Pink: BTKRF) (FSE: 0NB) ("QMET" or the "Company") is pleased to announce the confirmation of a second major natural hydrogen discovery in Nova Scotia. Building on its breakthrough results in the Apple Shulie Corridor, QMET and its partners — Quebec Innovative Materials Corp. (CSE: QIMC) and Institut National de la Recherche Scientifique ("INRS") — have now identified a significant new zone in the Springhill area.
The Springhill program collected 230 soil gas samples, returning 17 results above 400 ppm hydrogen (H₂), including three over 700 ppm (750, 778), and a peak of 1,652 ppm.
These findings complement QIMC's recent discoveries and further reinforce Nova Scotia's emergence as a district-scale natural hydrogen hub in North America, while underscoring QMET's expanding strategic footprint in this rapidly advancing sector.
Richard Penn, CEO of QMET, commented:
"The confirmation of a second major hydrogen zone at Springhill is another milestone in establishing Nova Scotia as a natural hydrogen hub in North America. Despite a partial survey, the results are strong, and this discovery strengthens QMET's district-scale position. Alongside our partners QIMC and INRS, we are proud to be advancing exploration at the forefront of this new energy frontier, unlocking the full potential of this emerging resource."
Geological Context
QMET hold 31 licenses along the northern margin of the Cumberland Basin within the Springhill-Salt Springs-Oxford-Pugwash-Fox Harbour-Wallace region. (see Figure 1) The licenses are generally located on the north limb of the Tetagouche Syncline along steeply dipping faults generally located at the boundaries of horst-like uplifts or within axial zones of narrow anticlines that separate intervening synclines. Windsor Group sediments hosting thick interbeds of salt and evaporitic formation outcrop at the margins of the synclines (see Figure 3).
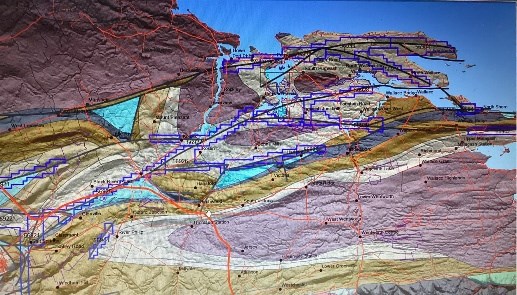
Figure 1 - Location of QMET Nova Scotia Hydrogen Claims on a geological map
To view an enhanced version of this graphic, please visit:
https://images.newsfilecorp.com/files/11423/266784_b54899f9144b5885_001full.jpg
At surface, the geometry of the individual synclines is further complicated by widely spaced north to northeast trending faults and by isolated down-dropped basins that host the youngest formational units of the Pictou Group. (See Figure 2) The northern limbs of synclines dipping steeply to the south appear as uplifted ridges exposing the basal units of Cumberland Group (the Boss Point formation) and the underlying Windsor Group. The fault contact below the Windsor Group against the younger units of the adjacent syncline also dips to the south. The structural complexity of the area is the result of transpressional tectonic forces resulting in right lateral EENE trending transcurrent faults with separated by local extensional regimes. This structural complexity is further modified by salt tectonic produced by mobilization of thicker salt-evaporites units by sedimentary deposition of thick Cumberland Group clastic formations. (see Figure 3) The salt diapers are modified by developing develop lateral flows forming basins where salt is withdrawn and ridges where salt rises to surface by diapiric rise of salt.
The region hosting the QMET licenses has been explored for oil and gas potential reservoirs in the last decade. Considerable reflective seismic studies had been undertaken in the region. Several wells were drilled. These wells aided in identifying the strongest reflective horizons and correlating them to contacts between certain stratigraphic formational units. These reflective profiles provide additional information with respect to the underlying structures which are now shown to differ substantially what is seen at surface. Faults identified cutting formations are observed to stop at overlying formations. It is possible to reconstruct different deformational periods and different ages of faulting. These studies are preliminary but will be of great importance in extracting how fluids move in the basins and where reservoirs may form.
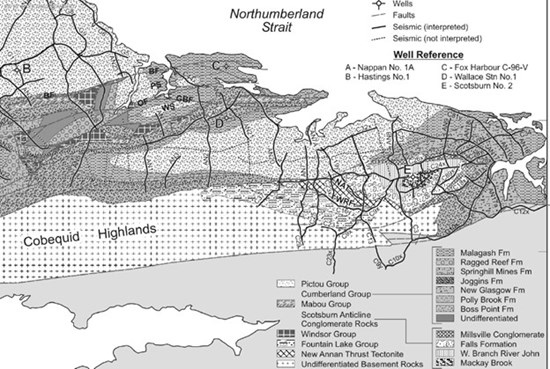
Figure 2 - Geologic map identifying major fault and fold structures and exposed stratigraphic formations that affect hydrogen gas diffusivity.
To view an enhanced version of this graphic, please visit:
https://images.newsfilecorp.com/files/11423/266784_b54899f9144b5885_002full.jpg
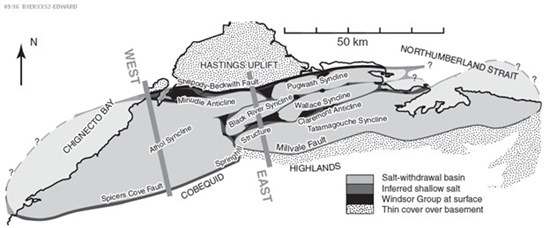
Figure 3 - Development of fold structures in area of interest by mobilization of salt-evaporite horizons in the Windsor Group.
To view an enhanced version of this graphic, please visit:
https://images.newsfilecorp.com/files/11423/266784_b54899f9144b5885_003full.jpg
The best hydrogen values were measured in the Springhill area where the Athol syncline is bent toward the north and terminated by a complex zone of faults that trend in a NNE direction. (See Figure 4) This Springhill structure appears to connect to the Oxford Fault which appears to be a crustal cutting fault which tap the composite basement formations containing basic volcanic and mafic intrusive units belonging to the Avalonian terrain.
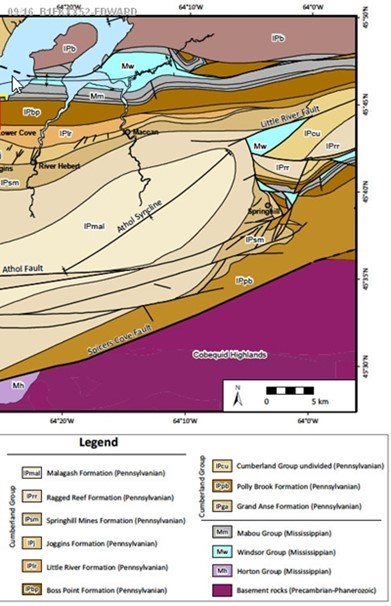
Figure 4 - Geological maps showing deformation of the Athol Syncline by development of strike slip transcurrent faults responding to trans compressional strain and flat lying thrusts. The northeast limb and axial region of the Athol Syncline is bent to the north and separated from highly faulted terrain northeast of Springhill by complex northerly trend fault structures called the Springhill Structure appears to connect to major crustal fault called the Oxford Fault.
To view an enhanced version of this graphic, please visit:
https://images.newsfilecorp.com/files/11423/266784_b54899f9144b5885_004full.jpg
Wildfire-Related Limitations
While wildfire alerts limited access to parts of the region, these early results already confirm Springhill as a second major zone. QMET partners, QIMC and INRS, plan to return to the Springhill-Salt Springs-Oxford-Pugwash-Fox Harbour-Wallace corridor in the Fall 2025 to complete the survey.
About Q Precious & Battery Metals Corp. (QMET)
QMET (CSE: QMET) is Canadian natural resource exploration company with
Exploration work conducted on the Colchester Project is overseen by Edward Procyshyn, P.GEO, a qualified expert in hydrogen exploration, he has reviewed, read and approved the technical content presented in this press release. Edward Procyshyn confirms that the methodologies employed, data presented, and interpretations made conform to current industry practices and standards relating to hydrogen exploration.
For further information, please contact:
Q Precious & Battery Metals Corp.
Richard Penn, CEO
778-384-8923
Email: richard@qmetalscorp.com
References:
Geology map with location QMET claims along structures defining syncline separated by narrow uplift anticlines or fault bounded horst like zones. Compiled at 1:50,000 scale by Nova Scotia Department of Mines. (Figure 1)
GEOLOGICAL SURVEY OF CANADA OPEN FILE 8937 -Seismic-reflection interpretation of the Carboniferous Cumberland Basin, northern Nova Scotia. P. Durling 2023 (Figure 2)
Waldron, J.W.F. et al 2013. Evaporite tectonics and the late Paleozoic stratigraphic development of the Cumberland Basin, Appalachians of Atlantic Canada GSA Bulletin, 125, pp. 945-960 (Figure 3)
Sedimentology and stratigraphy of the type section of the Pennsylvanian Boss Point Formation, Joggins Fossil Cliffs, Nova Scotia, Canada Michael C. Rygel et al 2024 doi: 10.4138/atlgeol.2015.001 (Figure 4)
Forward-Looking Statements
This press release contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of applicable Canadian securities legislation, including but not limited to statements regarding: exploration potential, geological characteristics, potential hydrogen discoveries, leveraging known geological conditions, replicating successful exploration models, expanding strategic collaborations, and anticipated exploration plans, milestones, timelines, and benefits arising from the collaboration agreement with Quebec Innovative Materials Corp. (QIMC). Such forward-looking statements are subject to numerous risks, uncertainties, and assumptions, including but not limited to: potential delays; geological uncertainties and the speculative nature of mineral and hydrogen exploration; actual exploration results differing materially from expectations; inability to replicate prior exploration successes or geological conditions of other projects; availability of financing; volatility of commodity prices; competition and market conditions affecting hydrogen and mineral exploration; operational and technological risks; unforeseen environmental and permitting challenges; legal and contractual uncertainties; general business, economic, competitive, political, and social uncertainties; and the risk that anticipated benefits of the collaboration with QIMC will not be realized. Although QMET believes these statements and expectations reflected therein are based upon reasonable assumptions as of the date hereof, there can be no assurance that these assumptions will prove accurate, and actual results or developments may differ materially from those projected. Readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on forward-looking statements. The Company undertakes no obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statements contained herein, whether as a result of new information, future events, or otherwise, except as required by law.

To view the source version of this press release, please visit https://www.newsfilecorp.com/release/266784







